Setting up a VM on the remote PC for remote access
- On the remote Windows 10 PC, start Oracle VirtualBox.

- In the list of virtual machines, select a VM, e.g. Ubuntu19. Click Settings.
The Settings dialog box appears.
- Click Display and then the Remote Display tab.
- Toggle on the Enable Server field. In the Server Port field, type in an unused port e.g. 5000. Click OK.
- Click the black drop down arrow on the Start icon and choose Start Headless Start.

The Virtual machine is started without displaying any windows.
Connecting to the remote VM from a local PC
- Now on a local PC e.g. an Ubuntu 18.04, start up a RDP client e.g. Remmina Remote Desktop Client.
- Create a new Remote Desktop Profile.
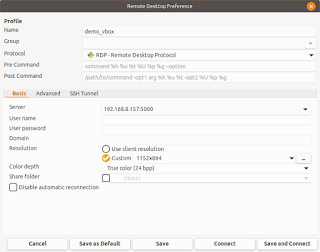
- In the Name field, type in a suitable name, e.g. demo_vbox.
- In the Protocol field, choose RDP - Remote Desktop Protocol.
- In the Server field, type in the IP address and port number of the remote Windows 10 computer, e.g. 192.168.123.123:5000.
- Choose an appropriate Resolution and Color depth.
- Save and connect to the VM.
The remote desktop is displayed.
If the remote VM cannot be connected successfully, then it is possible the remote Windows 10 PC's firewall is blocking the network port. To open the port, the following steps can be done.
- On Windows 10, click the Start button and then the Settings icon.
The Settings dialog box appears.
- Click Windows Security. Click Firewall and network protection.
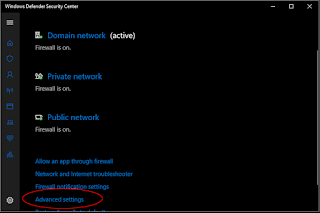
- Scroll down and click Advanced settings.
The Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security on Local Computer dialog box appears.
- Click Inbound Rules.

- Scroll down and ensure the vboxheadless rule exists and enabled. If not create a new rule and enable the selected port e.g. 5000.







