The following code snippet show how to use the library's ShapefileDataReader to read a Shapefile. In the example, all the database records and the Shape geometries are read into a features collection.
using GisSharpBlog.NetTopologySuite.Features;
using GisSharpBlog.NetTopologySuite.Geometries;
using GisSharpBlog.NetTopologySuite.IO;
using GeoAPI.Geometries;
...etc....
GeometryFactory factory = new GeometryFactory();
ShapefileDataReader shapeFileDataReader = new ShapefileDataReader(shpFilename, factory);
//Display the shapefile type
ShapefileHeader shpHeader = shapeFileDataReader.ShapeHeader;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Shape type: {0}", shpHeader.ShapeType));
//Display the min and max bounds of the shapefile
IEnvelope bounds = shpHeader.Bounds;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Min bounds: ({0},{1})", bounds.MinX, bounds.MinY));
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Max bounds: ({0},{1})", bounds.MaxX, bounds.MaxY));
//Display summary information about the Dbase file
DbaseFileHeader header = shapeFileDataReader.DbaseHeader;
Console.WriteLine("Dbase info");
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} Columns, {1} Records", header.Fields.Length, header.NumRecords));
for (int i = 0; i < header.NumFields; i++)
{
DbaseFieldDescriptor fldDescriptor = header.Fields[i];
Console.WriteLine(string.Format(" {0} {1}", fldDescriptor.Name, fldDescriptor.DbaseType));
}
//Reset the pointer to the start of the shapefile, just in case
//shapeFileDataReader.Reset();
//Read through all records of the shapefile (geometry and attributes) into a feature collection
ArrayList features = new ArrayList();
while (shapeFileDataReader.Read())
{
Feature feature = new Feature();
AttributesTable attributesTable = new AttributesTable();
string[] keys = new string[header.NumFields];
IGeometry geometry = (Geometry)shapeFileDataReader.Geometry;
for (int i = 0; i < header.NumFields; i++)
{
DbaseFieldDescriptor fldDescriptor = header.Fields[i];
keys[i] = fldDescriptor.Name;
attributesTable.AddAttribute(fldDescriptor.Name, shapeFileDataReader.GetValue(i));
}
feature.Geometry = geometry;
feature.Attributes = attributesTable;
features.Add(feature);
}
//Close and free up any resources
shapeFileDataReader.Close();
shapeFileDataReader.Dispose();
It is important to free up any resources used by calling the Close and Dispose methods, especially if you want to apply any file based operations e.g. deleting or renaming onto the Shapefile.
The following screenshot shows an example output from the code snippet.
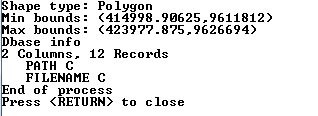
The ShapefileDataWriter class can be used to create a Shapefile. It seems that the class can only create new Shapefiles and there are no methods append to an existing Shapefile. The following code snippet shows how to write features with geometry and attributes into a Shapefile.
//Create a new shapefile from features
GeometryFactory outGeomFactory = new GeometryFactory();
//The constructor will append a ".shp" extension to the input filename so the 1st argument should not have an extension at all
string outShpFilenameNoExt = Path.Combine(Path.GetDirectoryName(outShpFilename), Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(outShpFilename));
ShapefileDataWriter writer = new ShapefileDataWriter(outShpFilenameNoExt, outGeomFactory);
DbaseFileHeader outDbaseHeader = ShapefileDataWriter.GetHeader((Feature)features[0], features.Count);
writer.Header = outDbaseHeader;
writer.Write(features);
