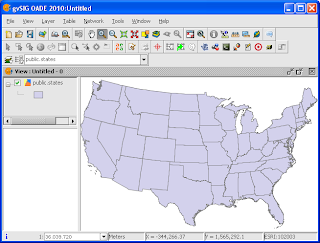
In order for gvSIG to access and manipulate features in PostGIS, a GeoDB connection must be made first as shown below.
- Start gvSIG OADE 2010. Create a new View with the desired coordinate system, e.g. Albers Equal Area. Open the view.

- Select View | Add Layer.
The Add Layer dialog box appears.
- Click the GeoDB tab.
- In the Connection field, click the New Connection button on the right.|
The Connection Settings dialog box appears.
- In the Connection name field, type in a name e.g. PostGISConn1.
- In the Driver field, choose PostGIS JDBC Driver.
- In the Server URL or IP field, type in the address name or the IP address e.g. 192.168.1.99.
- In the Database name field, type in the PostGIS database name e.g. gdotest.
- In the User field, type in the database user name e.g. gdouser.
- In the Password field, type in the password of the database user e.g. gdouser.
- Click OK.
If the values are correctly filled, the database would be connected to gvSIG. A list of tables appear.
- In the table list field, toggle on one or more spatial tables e.g. public.states.
- Click Ok.
The selected table(s) are displayed in the View.